How Colonialism Invented Food Insecurity in West Africa
Sapiens
NOVEMBER 12, 2024
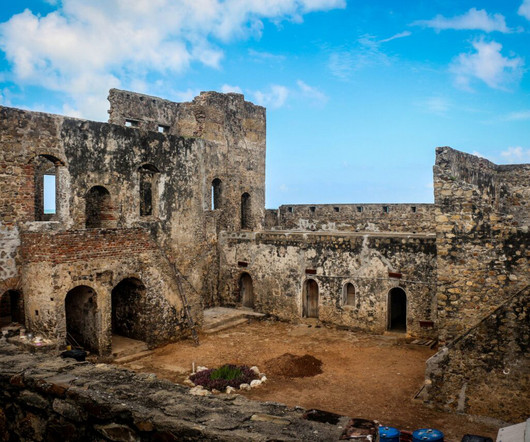
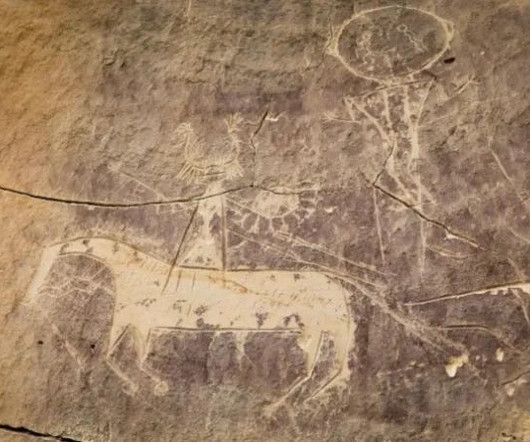
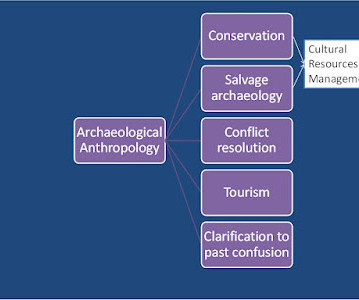
Archaeological evidence and Oral Histories show people in what is today Ghana lived sustainably for millennia—until European colonial powers and the widespread trade of enslaved people changed everything. I felt compelled to share this story as an example of the power of archaeology to shift perspectives.















Let's personalize your content