Tracing the Huns’ Genetic Legacy: A Eurasian Patchwork of Ancestry
Anthropology.net
FEBRUARY 24, 2025
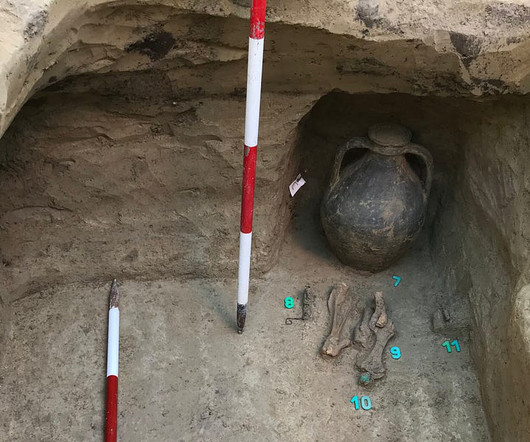
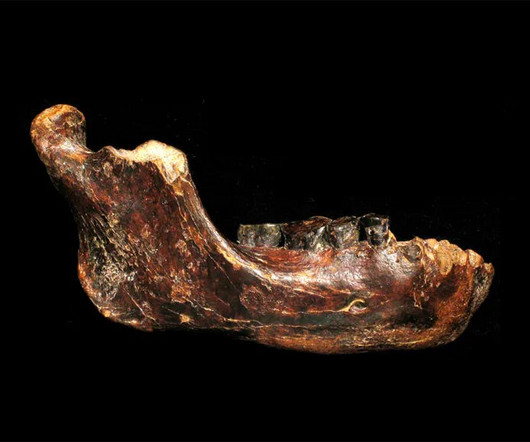
Credit: Boglárka Mészáros, BHM Aquincum Museum A team of geneticists, archaeologists, and historians from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and the HistoGenes project examined the DNA of 370 individuals dating from the 2nd century BCE to the 6th century CE, spanning sites from Mongolia to Central Europe.

















Let's personalize your content