Unveiling Homo juluensis: A New Chapter in Human Evolution
Anthropology.net
NOVEMBER 30, 2024
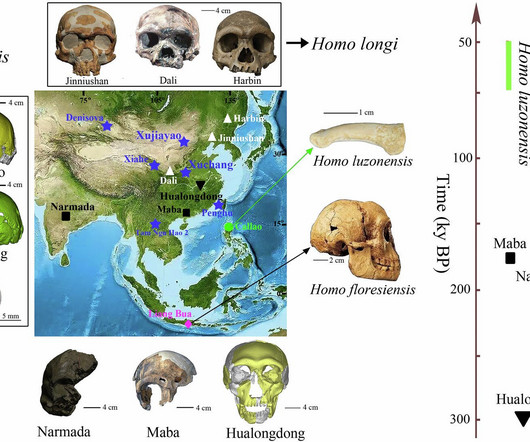
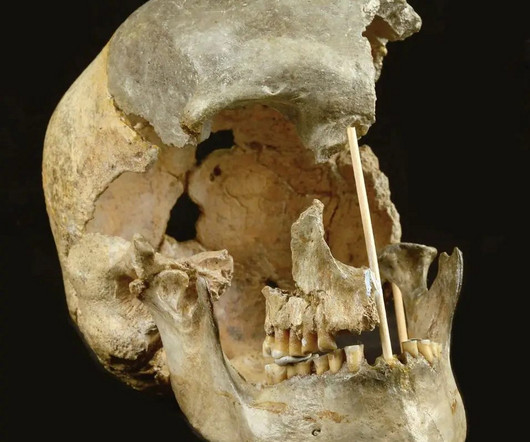
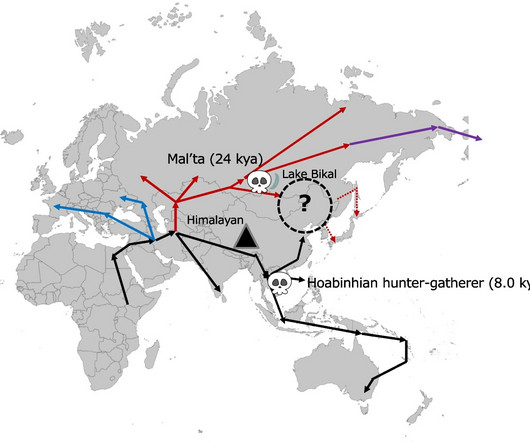
Discovery of a Potential New Human Species A groundbreaking study published in Nature Communications 1 has proposed the existence of a new human species, Homo juluensis. This ancient hominin, believed to have lived in eastern Asia between 300,000 and 50,000 years ago, is a significant addition to our understanding of human evolution.


























Let's personalize your content